DW Spectrum User Manual
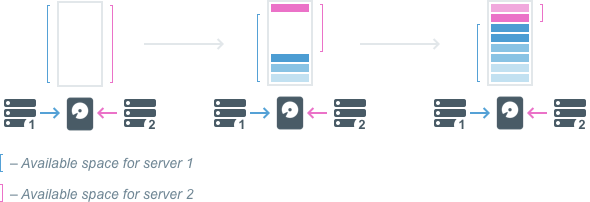
Video from a camera is always written to the server to which the camera is connected. Cameras can be moved between servers but the recorded video stays where it was and never moves with the camera. New video is written on the new server. Recorded video is called archive.
If a server has multiple drives, video archive is divided between them in order to improve reliability and balance the load on each drive. Nevertheless, even when different parts of the archive are stored on different drives or on different servers, video playback is seamless.
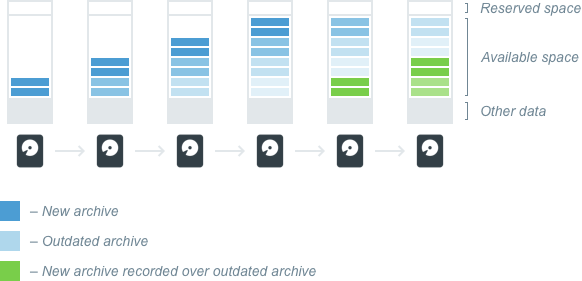
Other data is storage space occupied by data that isn't from the VMS, this storage space is never recorded on. In addition, a certain amount of the total capacity is reserved space that will not be used for recording. Numbers vary depending on the software version, server configuration; typically 10-30 GB is reserved for local storage and 50-100 GB is reserved for external storage.
Available Space
The remaining disk storage is considered available space – whether it is currently recorded on or is currently free space. Archive is recorded according to available space.
If there is no available space on a given storage device, the system will automatically delete outdated recordings in order to free space for new archive. By default the oldest archive is deleted first. However, there are two special properties a given camera can be granted that affect archive retention. One prevents archive from being deleted before a certain number of days has elapsed. The other requires that archive be deleted after a certain number of days has elapsed. These are the only cases in which the system will actively determine storage deletion.
Schematically, storage life cycle can be illustrated like this:
Storing Archive on Multiple Drives
Servers can have any number of storage devices. Recording to some can be disabled manually, or automatically when they are too small or are the main OS partition. USB drives are disabled by default, but can be enabled manually (though for ARM devices they can be enabled by default).
Enabled drives can be one of two types – main or backup type. Main storage is used to record archive, backup is used to store extra copies of some recordings. At any given moment, a drive can be assigned only one type, but because it is possible to change a drive's type, it is therefore possible to have different types of recording (main and backup) on one drive.
If there are multiple storage locations of the same type (main or backup) on a server, recorded archive will be split between them in proportion to their available space, as shown below:
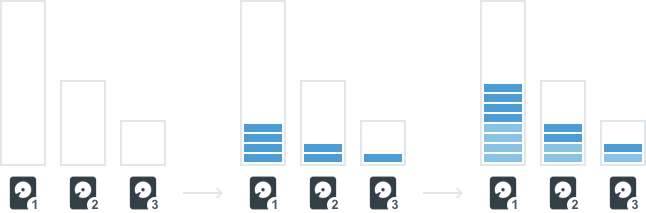
Note that when there are multiple storage locations of the same type on a server, recorded archive is distributed separately by type in proportion to the available space for each type.
Write bitrate (the amount of data that is processed per unit of time) will correlate with the amount of free space – in the illustration above disk 1 will have a higher bitrate than the others.
Remember that the distribution of recorded data is dependent on the amount of available space, not free space. If you have two similar drives, but part of drive #2 is occupied by some other data, recording speed will be higher for the drive #1 because the amount of available space for this drive is higher. Also, because archive recorded by the System does not reduce the amount of available space, recording speed doesn’t depend on how much available space is currently used.

For example, you have two similar drives, and both are already full. You add a third drive with the same amount of available space as the first two but completely empty. Distribution of recorded data is dependent on the amount of available space, so new recordings will be distributed evenly between all three drives. Even though there is plenty of free space on the third drive, outdated footage on the first two drives will be deleted to free up space for new recordings – archive must to be split evenly between all three drives because they have the same amount of the available space.

This is done to balance drive usage and to avoid a situation where all cameras are being written to one drive, which might not have enough speed to record such an amount of data.
Servers Sharing the Same Drive
It is possible to set up recording from multiple servers to the same drive. However, it is very important to split the drive into different partitions and attach separate partitions to each server so that archive written by one server cannot be deleted by another.
If you add one partition to multiple servers, they both will treat free space on that drive as available and will use it for recording. Data recorded by one server will be considered “other data” by the other server, and will reduce the amount of available space but will not be overwritten. However, if multiple servers use the same folder and the archive for any one of them is reindexed (see "Reindexing Archive") archive footage from the other servers can be deleted.
If different servers have different recording speeds, it will lead to a situation where storage is divided unequally. After storage is filled with archive, each server will manage only the space that is occupied by its own data, as shown in the diagram below.